Database
1
2
3
4
5
| SHOW DATABASES;
CREATE DATABASE <database name>
DROP DATABASE <database name>
USE <database name> -- 사용할 데이터베이스를 지정한다.
SELECT <database name> -- 현재 사용중인 데이터베이스명을 알려준다.
|
Table
CREATE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| CREATE TABLE cats (
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'unnamed'
, age INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 99
);
CREATE TABLE cats2 (
cat_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
, name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
, age INT NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL
, first_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
, last_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
, middle_name VARCHAR(255)
, age INT NOT NULL
, current_status VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'employed'
, PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
SHOW COLUMNS FROM <table name> -- 필드와 타입 등 정보를 출력한다.
== DESCRIBE <table name>
== DESC <table name>
DROP TABLE <table-name>;
|
ALTER
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| -- 컬럼 추가
alter table companies
add column city varchar(20);
alter table companies
add column employee_count tinyint not null default 1;
-- 컬럼 삭제
alter table companies
drop column city;
-- 테이블명 변경
alter table company rename to companies;
-- == rename table companies to company;
-- 컬럼명 변경
alter table companies
rename column employee_count to ec;
-- 제약조건 수정
alter table companies
modify name varchar(100) not null default 'unknown';
-- 컬럼명 변경 && 데이터타입 수정
alter table companies
change address adrs varchar(100);
-- 제약조건 추가
alter table users
add constraint positive_number check (age > 0);
-- 제약조건 삭제
alter table users
drop constraint positive_number;
-- 컬럼순서 변경
-- ALTER TABLE 테이블명 MODIFY COLUMN 컬럼명 데이터타입 제약조건 FIRST/AFTER 컬럼명;
alter table `user`
modify column bloodType varchar(2) not null after age;
-- 컬럼타입변경
alter table `user`
modify column id varchar(30) unique not null;
|
INSERT
INSERT INTO <table name> (field names…) values (values…)
1
2
3
4
5
| INSERT INTO cats (name, age)
VALUES
('Meatball', 5),
('Turkey', 1),
('Potato Face', 15);
|
UPDATE
update <table name> set = , ... where ...
1
2
3
4
5
6
| update
shirts
set
shirt_size = 'XS'
, color = 'off white'
where color = 'white';
|
개념정리
- 데이터베이스 : 접근 가능한 인터페이스를 가진 컴퓨터화 된 데이터의 구조화된 집합.
- 관계형 데이터베이스 ( Relational Databases ) - MySql, Oracle, SqLite, PostgreSql…
- 엔트리 == 행. 즉, 각각의 데이터.
- where 조건을 먼저 찾은 후 select 한 컬럼을 출력한다. where 절 안 컬럼은 select 후의 컬럼에 포함될 필요가 없다. 서로 독립적이다.
- CLI 에서 sql 소스를 import 할 수 있다. mysql> source C:/Users/withy/Downloads/book_data.sql;
- DISTINCT 는 SELECT 에 출력할 모든 필드에 적용이 된다.
자주 사용하는 문자열 함수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| select concat_ws('-', 'oh', 'jeong', 'gil'); -- oh-jeong-gil
select substring('hello world', 7, 5); -- world
select substring('hello world', -5); -- world
select reverse('abcde'); -- edcba
select char_length('훌륭한 개발자'); -- 7
select length('훌륭한 개발자'); -- 19
select ucase('hello'); -- HELLO
select lcase('HELLO'); -- hello
select insert('Hello World', 6, 0, ' Jeong\'s'); -- Hello Jeong's Wrold
select left('OmgHahaLol~~', 3); -- Omg
select right('OmgHahaLol~~', 5); -- Lol~~
select repeat('ha', 3); -- hahaha
select trim(' jeong '); -- jeong
select trim(leading '.' from '.....this is for you..'); -- this is for you..
select trim(trailing '.' from '.....this is for you..'); -- .....this is for you
select trim(both '.' from '.....this is for you..'); -- this is for you
|
substring() == substr()
char_length() : 글자 길이 반환
length() : 바이트 길이 반환
ucase() == upper()
lcase() == lower()
집계함수 (Aggregate function)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| -- count()
select count(distinct author_fname) from books; -- 고유값의 갯수를 알고 싶을 경우.
-- group by
select
title
, avg(rating)
from full_reviews
group by title
having count(rating) >= 2; -- having : group by 로 생성한 그룹을 필더링해준다.
-- min(), max(), sum(), avg()
select
title
, pages
from books
where pages = (select max(pages) from books);
select
author_fname
, author_lname
, min(released_year)
from books
group by author_fname, author_lname;
-- ==
select
concat_ws(' ', author_fname, author_lname) as name
, count(title)
, min(released_year)
, max(released_year)
, sum(pages)
, avg(pages)
from books
group by name;
|
count() : null 값을 제외한 괄호 안 컬럼 행에 들어있는 값의 갯수를 출력한다.
group by : 그룹핑 후 집계함수(count, min, max, avg)와 함께 쓰인다.
데이터 타입 (Data Type)
문자 데이터 유형
- varchar(100) : variable + character
- char(5) : 모든 문자열의 크기가 5. 문자열이 5보다 작은 데이터를 INSERT 시, 나머지 부분은 공백으로 채워진다. 데이터의 크기가 정해져 있으면 메모리 효율상 char를 사용하는게 낫다.
숫자 데이터 유형
날짜와 시간과 관련된 데이터 유형
- date : ‘YYYY-MM-DD’
- time : ‘HH:MM:SS’
- datetime : ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’
- curdate() == current_date() ( ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ )
- curtime() == current_time() ( ‘HH:MM:SS’ )
- now() == current_timestamp() ( ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| INSERT INTO people (name, birthdate, birthtime, birthdt) VALUES ( 'Hazel', CURDATE(), CURTIME(), NOW() );
SELECT
birthdate,
day(birthdate), -- day() == dayofmonth()
dayofweek(birthdate),
dayofyear(birthdate)
FROM people;
SELECT
birthdate,
monthname(birthdate),
year(birthdate)
FROM people;
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%W'); -- Saturday. select dayname(current_date);
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(CURDATE(), '%m/%d/%Y'); -- 09/30/2023
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%M %D at %h:%i'); -- September 30th at 10:30
|
- select datediff(curdate(), ‘1993-01-03’); – 두 날짜간 일수 차이를 출력한다.
- select date_add(‘1993-01-03’, interval 2 day); – 1993-01-05
- select date_sub(‘1993-01-03’, interval 10 year); – 1983-01-03
- select timediff(curtime(), ‘07:00:00’); – 현재 시간을 기준으로 오전 7시부터 얼마나 깨어 있었는지 출력한다.
- select name, birthdate, year(birthdate + interval 21 year) as willBe21 from people; – 날짜 +/- 시 interval 을 사용한다.
- timestamp : range ( 1970-01-01 ~ 2038-01-19 ), datetime 보다 메모리를 덜 차지.
- datetime : range ( 1000-01-01 ~ 9999-12-31 )
1
2
3
4
5
| create table captions (
text varchar(150)
, created_at timestamp default current_timestamp
, updated_at timestamp on update current_timestamp
);
|
default current_timestamp : 따로 INSERT 하지 않아도 현재 시간이 데이터로 입력된다.
on update current_timestamp : 행에서 어떤 열이 변경될 때마다 그 열을 current_timestamp == now() 로 업데이트한다.
날짜비교
- mysql 은 문자열과 날짜를 비교해서 결과를 알려주지만 정확하지 않을 수도 있다.
1
2
3
| select now() > cast('12:03:00' as time); -- cast 로 문자를 시간으로 변경하여 값을 비교한다.
SELECT * FROM people WHERE HOUR(birthtime) BETWEEN 12 AND 16;
|
제약조건
unique
1
2
3
4
| CREATE TABLE contacts (
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
, phone VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL UNIQUE
);
|
Primary Key 와 Unique 제약조건을 하나의 컬럼에 동시에 쓰지는 않는다.
1
2
3
4
5
| create table companies (
name varchar(50) not null
, address varchar(100) not null
, constraint test unique (name, address) -- name 과 address 가 모두 중복일 경우 test 제약조건 위반.
);
|
check
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| CREATE TABLE users (
username VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL
, age INT
, CONSTRAINT age_over_18 CHECK(age > 18) -- 제약조건명을 설정할 수 있다.
);
CREATE TABLE palindromes (
word VARCHAR(100)
, CONSTRAINT word_is_palindrome CHECK(REVERSE(word) = word)
)
|
일대다 ( One To Many & Many:Many & Joins )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| create table customers (
customer_id int primary key auto_increment
, first_name varchar(50) not null
, last_name varchar(50) not null
, email varchar(100)
);
create table orders (
order_id int auto_increment
, order_date timestamp default current_timestamp
, amount decimal(8,2) not null
, customer_id int
, primary key (order_id)
, foreign key (customer_id) references customers(customer_id)
on delete cascade
);
|
on delete cascade : 부모의 데이터가 삭제될 경우, 자식테이블 내 해당 데이터를 참조하고 있는 데이터도 삭제한다. => 즉 부모데이터를 삭제 가능하게 하며 그와 관련된 데이터는 모두 삭제된다.
inner join
1
2
3
4
5
6
| select
c.first_name
, c.last_name
, sum(o.amount)
from customers c inner join orders o on c.customer_id = o.customer_id
group by c.first_name, c.last_name;
|
left/right join
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| select
c.first_name
, c.last_name
, ifnull(sum(o.amount), 0) as 'money_spent'
from customers c left join orders o on c.customer_id = o.customer_id
group by c.first_name, c.last_name;
select
title as 'unreviewed series'
from series s left join reviews r on s.id = r.series_id
where r.rating is null;
|
VIEW
- view를 활용하여 결과를 반환하는 쿼리를 저장하고 이름을 지정한 다음 실제 테이블처럼 취급할 수 있다. => 관계성이 깊고 자주 사용하는 테이블들을 JOIN 하여 새 VIEW 테이블을 만들고, Group By 혹은 Where 를 사용해서 VIEW를 통해 원하는 데이터를 가져올 수 있다.
- view 는 테이블 기능을 가지고 있지만 실제 테이블은 아니다. view 안 데이터는 삽입, 업데이트, 삭제가 안된다. (일부의 view 에서만 가능)
1
2
3
4
| CREATE VIEW full_reviews AS
SELECT title, released_year, genre, rating, first_name, last_name FROM reviews
JOIN series ON series.id = reviews.series_id
JOIN reviewers ON reviewers.id = reviews.reviewer_id;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| -- 해당 view 가 존재하면 update, 그렇지 않다면 해당 view 를 생성.
create or replace view ordered_series as
select * from series order by released_year desc;
-- 해당 view 수정.
alter view ordered_series as
select * from series order by released_year desc;
-- 해당 view 삭제
drop view ordered_series;
|
WITH ROLLUP
1
2
3
4
5
6
| select
title
, avg(rating)
, count(rating)
from full_reviews
group by title with rollup;
|
with rollup : group by 와 함께 쓰이며 그룹화 된 정보를 바탕으로, 사용된 집계함수에 대한 전체 데이터를 하위에 출력한다.
SQL MODE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| -- 글로벌 범위의 sql 모드 (영구적인 변경을 원할 경우)
select @@global.sql_mode;
-- ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY ( group by 뒤에 있어야할 컬럼이 있지 않을경우 오류 발생 )
-- , STRICT_TRANS_TABLES ( 컬럼에 맞는 데이터타입이 들어가게 해준다. )
-- , NO_ZERO_IN_DATE ( 날짜 0월 0일 방지 )
-- , NO_ZERO_DATE
-- , ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO ( 0으로 나눌수 없다. )
-- , NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
-- 세션 범위의 sql 모드
select @@session.sql_mode;
select 3/0; -- warning : Division by 0
-- Division by 0 warning 을 나오게 하고 싶지 앟을 경우 sql_mode에 RROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO 을 제외한 나머지 설정을 set 해준다.
set session sql_mode = 'ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION';
|
SQL MODE 에는 글로벌 모드, 세션 모드가 있다.
Division by 0 경고를 나오게 하고 싶지 앟을 경우 sql_mode에 RROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO 을 제외한 나머지 설정들을 set 해준다.
윈도우 함수 ( Window Function )
over()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| select
department
, min(salary) over(partition by department)
, max(salary) over(partition by department)
, avg(salary) over(partition by department)
, avg(salary) over() -- 전체 평균 급여가 각 행마다 출력된다.
from employees e
select
department
, count(*) over(partition by department)
from employees e ;
|
집계함수 뒤 over() 괄호 안에 명시되어있는 값이 없으면 전체를 기준으로 값을 산출해 각 행에 출력한다.
집계함수 뒤 over ( partition by ) : 그룹을 짓지 않고 입력된 컬럼명으로 가상의 그룹을 지어 그에 해당하는 값을 각 행에 출력한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
| select
emp_no
, department
, salary
, sum(salary) over(partition by department order by salary desc)
from employees e ;
|
부서별로 나뉜 상태에서 급여가 rolling 처럼 다음 행의 값은 이전 행의 모든 봉급의 합이 된다.
- min max sum avg 는 집계함수로 group by 와 쓰이거나 window 함수로 사용가능하다.
only window function
rank(), row_number(), dense_rank()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| select
emp_no
, department
, salary
, row_number() over(partition by department order by salary desc) as department_rowNumber
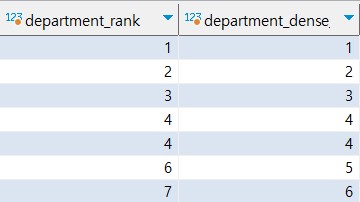
, rank() over(partition by department order by salary desc) as department_rank -- 부서별로 순위를 매긴다. (건너뛰는 숫자가 존재한다.)
, dense_rank() over(partition by department order by salary desc) as department_dense_rank -- 공동 순위가 있을 시, 다음 순위는 그 다음 번호로 매겨진다. (건너뛰는 숫자가 없다)
, rank() over(order by salary desc) as overall_rank -- partition 으로 나누지 않아, 전체 순위를 매긴다.
from employees e
order by department;
|
![]()
ntile()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| select
emp_no
, department
, salary
, ntile(4) over(partition by department order by salary desc)
, ntile(4) over(order by salary desc)
from employees e
order by department ;
|
ntile() : 괄호 안의 표현식 값을 기준으로 나눠 순위를 매긴다.
first_value()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| select
emp_no
, department
, salary
, first_value(emp_no) over(order by salary desc) as 'first_value' -- 급여가 가장 높은 emp_no가 보다 낮은 하위행에 모두 찍힌다.
, nth_value(emp_no, 20) over(order by salary desc) as 'nth_value' -- 높은 급여를 기준으로 급여가 20번째인 emp_no가 모든 하위 행에 찍힌다.
, first_value(emp_no) over(partition by department order by salary desc) as 'first_value_by_department' -- 급여가 가장 높은 emp_no가 부서별로 찍힌다.
from employees e
order by department ;
|
괄호 안의 표현식 값이 첫번째 행에서 반환된다.
lead(), lag()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| select
emp_no
, department
, salary
-- , lag(salary) over(order by salary desc) -- 괄호 안의 표현식 값 이전 행의 값을 출력한다.
, salary - lag(salary) over(partition by department order by salary desc) -- 부서별 이전 행의 급여와의 차이를 구한다.
from employees e;
|
lead(), lag() : 주로 한 행과 그 전 또는 다음 행 간의 차이를 찾기 위해 사용한다.
마지막 과제 ( Instagram Clone )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
| -- 1. 가장 오래된 유저 5명을 찾아라.
select * from users order by created_at asc limit 5;
-- 2. 어떤 요일, 시간에 광고를 올리는게 좋을까? 어느 요일에 회원가입을 많이 했는가?
select
dayname(created_at) as dateValue
, count(*) as cnt
from users
group by dateValue
order by cnt desc;
-- 3. 사진을 게시하지 않은 유저를 찾아라.
select
u.username
from users u left join photos p on u.id = p.user_id
where p.user_id is null;
-- 4. 가장 인기있는 사진과 게시한 유저를 찾아라.
-- mine
select
u.id as userId
, u.username
, p.id as photoId
, p.image_url
from photos p inner join users u on u.id = p.user_id
where p.id = (
select
a.photo_id
from (
select
photo_id
, count(photo_id) as cnt
from likes l
group by photo_id
order by cnt desc
limit 1
) a
);
-- teacher ( 조인을 해서 가져올 시 다양한 데이터를 가공해서 뿌려올 수 있다. ( 좋아요 수 등.. ) )
select
p.user_id
, u.username
, p.id as 'photo id'
, p.image_url
, count(l.photo_id) as total
from photos p
inner join likes l on p.id = l.photo_id
inner join users u on u.id = p.user_id
group by p.id
order by total desc
limit 1;
-- 5. 평균적으로 유저가 게시물을 얼마나 많이 올리는가? 전체 게시물 수 / 전체 유저 수
-- mine
select
count(p.id) / (select count(id) from users) as avg
from photos p;
-- teacher
SELECT
(SELECT Count(*) FROM photos)
/ (SELECT Count(*) FROM users) AS avg;
-- 6. 가장 많이 사용되는 해시태그 5개를 찾아라.
select
p.tag_id
, t.tag_name
, count(p.photo_id) as total
from photo_tags p inner join tags t on p.tag_id = t.id
group by p.tag_id, t.tag_name
order by total desc
limit 5;
-- 7. 웹사이트에 존재하는 모든 사진에 좋아요를 누른 유저를 찾아라.
-- mine
select
u.id
, u.username
from
(
select
user_id
, count(*) as total
from likes
group by user_id
order by total desc
) a
inner join users u on a.user_id = u.id
where a.total = (select count(*) from photos)
order by u.username;
-- teacher
select
u.username
, count(*) as 'like_count'
from users u
inner join likes l on u.id = l.user_id
group by u.id
having like_count = (select count(*) from photos)
order by u.username;
-- 1. 좋아요를 누르지 않은 유저는 해당되지 않으므로 inner join
-- 2. 그룹화 된 후, having 절로 필터링하는 법을 잊지 말자.
|