Batch
- 작업이 중단되었을 경우, 중단점 파악 가능. 이로써 중복 작업을 피할 수 있음
- 읽기, 처리, 쓰기를 다 읽을때까지 반복
- 한 번에 다 읽지 않는 이유
- 메모리 부족 오류 발생 가능성
- 실패시 위험성 크고 속도저하 문제 발생
- 한 번에 다 읽지 않는 이유
메타 데이터(했던 작업을 기록하는 테이블)- 배치는 데이터를 단위별로 끊어서 읽기에 작업 지점을 기록해야한다.
Spring Batch 모식도
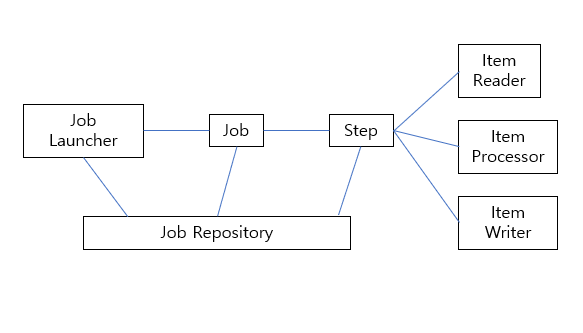
- JobLauncher: 하나의 배치 작업을 실행시키는 시작점
- Job: 읽기, 처리, 쓰기 과정을 정의한 배치 작업
- Step
- 읽기, 처리, 쓰기 작업을 정의한 부분
- 하나의 Job에서 여러 과정 진행 가능하기에 1 대 N 구조를 가진다.
- JobRepository: 메타 데이터를 기록하는 부분
구현 순서
- 데이터베이스 2개
- DB1: 메타 데이터
- DB2: 배치 처리 데이터
- 데이터베이스 Config 파일 작성
- Job 생성 → Step 생성 → Reader, Processor, Writer 생성
ItemStreamReader
- 배치에서 데이터를 읽는 Reader
- 작업중인 부분을 메타 데이터에 저장해야하고 처리한 부분은 스킵해야하기 때문에 스프링 배치에서 가장 중요부분이다.
- 스프링 배치에서 다양한 Reader 구현체 제공
- 하나의 데이터를 읽어올 때 read() 메소드 호출
1
2
3
public interface ItemStreamReader<T> extends ItemStream, ItemReader<T> {
}
1
2
3
4
5
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ItemReader<T> {
@Nullable
T read() throws Exception, UnexpectedInputException, ParseException, NonTransientResourceException;
}
read(): 하나의 데이터를 읽어올 때 해당 메소드 호출
1
2
3
4
5
public interface ItemStream {
default void open(ExecutionContext executionContext) throws ItemStreamException {}
default void update(ExecutionContext executionContext) throws ItemStreamException {}
default void close() throws ItemStreamException {}
}
open(ExcutionContext ex): Step에서 처음 reader를 호출하면 시작되는 부분으로 초기화나 이미 했던 작업의 경우 중단점까지 건너뛰도록 설계하는 부분
update(ExcutionContext ex): read() 호출 후 바로 호출. read()에서 처리한 작업 단위를 기록하는 용도
close(): 배치 작업이 완료되고 불려지는 메소드로 파일을 저장하거나 필드 변수를 초기화하는 메소드로 사용
ExecutionContext
- ItemStream의 open(), update()에 매개변수로 주입되는 있는 객체
- 배치 작업 처리시 기준점을 잡을 변수를 계속하여 트래킹하기 위한 저장소로 사용
Step
- 배치 작업을 처리하는 하나의 묶음
- Chunk 방식(Reader → Processor → Writer)
- 청크 값 10으로 설정시, Read X 10 → Process X 10 → Write
- Tasklet 방식
- 간단한 동작만하기에 단순 파일 삭제, 값 초기화 용도로만 사용된다.
- Chunk 방식(Reader → Processor → Writer)
Skip
- Step의 과정 중 예외가 발생하게 되면 예외를 특정 수 까지 건너 뛸 수 있도록 설정하는 방법
- e.g.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
@Bean public Step sixthStep() { return new StepBuilder("sixthStep", jobRepository) .<BeforeEntity, AfterEntity> chunk(10, platformTransactionManager) .reader(beforeSixthReader()) .processor(middleSixthProcessor()) .writer(afterSixthWriter()) .faultTolerant() .skip(Exception.class) .noSkip(FileNotFoundException.class) .noSkip(IOException.class) .skipLimit(10) .build(); } @Bean public Step sixthStep() { return new StepBuilder("sixthStep", jobRepository) .<BeforeEntity, AfterEntity> chunk(10, platformTransactionManager) .reader(beforeSixthReader()) .processor(middleSixthProcessor()) .writer(afterSixthWriter()) .faultTolerant() .skipPolicy(customSkipPolicy) .noSkip(FileNotFoundException.class) .noSkip(IOException.class) .build(); }
Retry
- Step의 과정 중 예외가 발생하게 되면 예외를 특정 수 까지 반복 할 수 있도록 설정하는 방법
- e.g.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
@Bean public Step sixthStep() { return new StepBuilder("sixthStep", jobRepository) .<BeforeEntity, AfterEntity> chunk(10, platformTransactionManager) .reader(beforeSixthReader()) .processor(middleSixthProcessor()) .writer(afterSixthWriter()) .faultTolerant() .retryLimit(3) .retry(SQLException.class) .retry(IOException.class) .noRetry(FileNotFoundException.class) .build(); }
Writer 롤백 제어
- Writer시 특정 예외에 대해 트랜잭션 롤백을 제외하는 방법
- e.g.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
@Bean public Step step1(JobRepository jobRepository, PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) { return new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository) .<String, String>chunk(2, transactionManager) .reader(itemReader()) .writer(itemWriter()) .faultTolerant() .noRollback(ValidationException.class) .build(); }
Step listener
- Step의 실행 전후에 특정 작업을 수행 시킬 수 있는 방법
- 로그를 남기거나 다음 Step이 준비가 되었는지, 이번 Step과 다음 Step이 의존되는 경우 변수 정리를 진행 가능
- e.g.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
@Bean public StepExecutionListener stepExecutionListener() { return new StepExecutionListener() { @Override public void beforeStep(StepExecution stepExecution) { StepExecutionListener.super.beforeStep(stepExecution); } @Override public ExitStatus afterStep(StepExecution stepExecution) { return StepExecutionListener.super.afterStep(stepExecution); } }; } @Bean public Step sixthStep() { return new StepBuilder("sixthStep", jobRepository) .<BeforeEntity, AfterEntity> chunk(10, platformTransactionManager) .reader(beforeSixthReader()) .processor(middleSixthProcessor()) .writer(afterSixthWriter()) .listener(stepExecutionListener()) .build(); }
Job
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
// 순차적 step 실행
@Bean
public Job footballJob(JobRepository jobRepository) {
return new JobBuilder("footballJob", jobRepository)
.start(playerLoad())
.next(gameLoad())
.next(playerSummarization())
.build();
}
// 조건에 따른 실행
@Bean
public Job job(JobRepository jobRepository, Step stepA, Step stepB, Step stepC, Step stepD) {
return new JobBuilder("job", jobRepository)
.start(stepA)
.on("*").to(stepB)
.from(stepA).on("FAILED").to(stepC)
.from(stepA).on("COMPLETED").to(stepD)
.end()
.build();
}
// Job listener: Job의 실행 전후에 특정 작업을 수행 시킬 수 있는 방법
@Bean
public JobExecutionListener jobExecutionListener() {
return new JobExecutionListener() {
@Override
public void beforeJob(JobExecution jobExecution) {
JobExecutionListener.super.beforeJob(jobExecution);
}
@Override
public void afterJob(JobExecution jobExecution) {
JobExecutionListener.super.afterJob(jobExecution);
}
};
}
@Bean
public Job sixthBatch() {
return new JobBuilder("sixthBatch", jobRepository)
.start(sixthStep())
.listener(jobExecutionListener())
.build();
}
JPA 성능 문제 및 JDBC
- 스프링 배치 read, write 부분을 JPA로 구성할 경우 JDBC 대비 처리 속도가 엄청나게 저하
- Writer의 경우 엄청난 영향을 끼치는데, 이유는 아래와 같다.
- Bulk 쿼리 실패
- Entity의 Id 생성 전략은 보통 IDENTITY로 설정하게 되는데, 이때 JPA IDENTITY 전략 때문에 bulk 쿼리 대신 각각의 수만큼 insert가 수행된다.
- Bulk 쿼리 실패
- e.g.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48
// Reader @Bean public RepositoryItemReader<BeforeEntity> beforeSixthReader() { return new RepositoryItemReaderBuilder<BeforeEntity>() .name("beforeReader") .pageSize(10) .methodName("findAll") .repository(beforeRepository) .sorts(Map.of("id", Sort.Direction.ASC)) .build(); } @Bean public JdbcPagingItemReader<BeforeEntity> beforeSixthReader() { return new JdbcPagingItemReaderBuilder<BeforeEntity>() .name("beforeSixthReader") .dataSource(dataSource) .selectClause("SELECT id, username") .fromClause("FROM BeforeEntity") .sortKeys(Map.of("id", Order.ASCENDING)) .rowMapper(new CustomBeforeRowMapper()) .pageSize(10) .build(); } // Writer @Bean public RepositoryItemWriter<AfterEntity> afterSixthWriter() { return new RepositoryItemWriterBuilder<AfterEntity>() .repository(afterRepository) .methodName("save") .build(); } @Bean public JdbcBatchItemWriter<AfterEntity> afterSixthWriter() { String sql = "INSERT INTO AfterEntity (username) VALUES (:username)"; return new JdbcBatchItemWriterBuilder<AfterEntity>() .dataSource(dataSource) .sql(sql) .itemSqlParameterSourceProvider(new BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<>()) .build(); }
출처: https://www.devyummi.com/page?id=66951d4d823bbb8bc327ba0e
