요청 매핑
PathVariable 다중 사용
1
2
3
4
5
@GetMapping("/mapping/users/{userId}/orders/{orderId}")
public String mappingPath(@PathVariable("userId") String userId, @PathVariable("orderId") Long orderId) {
log.info("mappingPath userId={}, orderId={}", userId, orderId);
return "pathVariable";
}
특정 파라미터 조건 매핑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/**
* 파라미터로 추가 매핑
* params="mode",
* params="!mode"
* params="mode=debug"
* params="mode!=debug" (! = )
* params = {"mode=debug","data=good"}
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-param", params = "mode=debug")
public String mappingParam() {
log.info("mappingParam");
return "ok";
}
특정 헤더 조건 매핑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/**
* 특정 헤더로 추가 매핑
* headers="mode",
* headers="!mode"
* headers="mode=debug"
* headers="mode!=debug" (! = )
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-header", headers = "mode=debug")
public String mappingHeader() {
log.info("mappingHeader");
return "ok";
}
파라미터 매핑과 비슷하지만, HTTP 헤더를 사용한다.
Postman으로 테스트해야 한다.
미디어 타입 조건 매핑 - HTTP 요청 Content-Type, consume
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/**
* Content-Type 헤더 기반 추가 매핑 Media Type
* consumes="application/json"
* consumes="!application/json"
* consumes="application/*"
* consumes="*\/*"
* MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE
*
* ex )
* consumes = "text/plain"
* consumes = {"text/plain", "application/*"}
* consumes = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-consume", consumes = "application/json")
public String mappingConsumes() {
log.info("mappingConsumes");
return "ok";
}
HTTP 요청의 Content-Type 헤더를 기반으로 미디어 타입으로 매핑한다.
만약 맞지 않으면 HTTP 415 상태코드(Unsupported Media Type)을 반환한다.
미디어 타입 조건 매핑 - HTTP 요청 Accept, produce
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/**
* Accept 헤더 기반 Media Type
* produces = "text/html"
* produces = "!text/html"
* produces = "text/*"
* produces = "*\/*"
*
* ex )
* produces = "text/plain"
* produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"}
* produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE
* produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-produce", produces = "text/html")
public String mappingProduces() {
log.info("mappingProduces");
return "ok";
}
HTTP 요청의 Accept 헤더를 기반으로 미디어 타입으로 매핑한다.
만약 맞지 않으면 HTTP 406 상태코드(Not Acceptable)을 반환한다.
요청 매핑 - API 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/mapping/users")
public class MappingClassController {
/**
* 회원 목록 조회: GET /mapping/users
*/
@GetMapping
public String users() {
return "get users";
}
/**
* 등록: POST /mapping/users
*/
@PostMapping
public String addUser() {
return "post user";
}
/**
* 회원 조회: GET /mapping/users/{userId}
*/
@GetMapping("/{userId}")
public String findUser(@PathVariable String userId) {
return "get userId=" + userId;
}
/**
* 회원 수정: PATCH /mapping/users/{userId}
*/
@PatchMapping("/{userId}")
public String updateUser(@PathVariable String userId) {
return "update userId=" + userId;
}
/**
* 회원 삭제: DELETE /mapping/users/{userId}
*/
@DeleteMapping("/{userId}")
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable String userId) {
return "delete userId=" + userId;
}
}
HTTP 요청 - 기본, 헤더 조회
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class RequestHeaderController {
@RequestMapping("/headers")
public String headers(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response
, HttpMethod httpMethod
, Locale locale
, @RequestHeader MultiValueMap<String, String> headerMap
, @RequestHeader("host") String host
, @CookieValue(value = "myCookie", required = false) String cookie
) {
log.info("request={}", request); // org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@14bede27
log.info("response={}", response); // org.springframework.web.context.request.async.StandardServletAsyncWebRequest$LifecycleHttpServletResponse@403568ce
log.info("httpMethod={}", httpMethod); // GET
log.info("locale={}", locale); // ko_KR
log.info("headerMap={}", headerMap); // {host=[localhost:8080], connection=[keep-alive], sec-ch-ua=["Chromium";v="124", "Google Chrome";v="124", "Not-A.Brand";v="99"]... }
log.info("header host={}", host); // localhost:8080
log.info("myCookie={}", cookie); // null
return "ok";
}
}
@RequestHeaderMultiValueMap<String, String> headerMap: 모든 HTTP 헤더를 MultiValueMa식으로 조회한다.
@RequestHeader(“host”) String host: http 헤더 안 host 정보만 조회한다.
@CookieValue(value = “myCookie”, required = false) String cookie: 특정 쿠키를 조회한다.
MultiValueMap: HTTP header, HTTP 쿼리 파라미터와 같이 하나의 키에 여러 값을 받을 때 사용한다.
HTTP 요청 파라미터 - @RequestParam
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v1")
public void requestParamV1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
int age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("age"));
log.info("username = {}, age = {}", username, age);
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v2")
public String requestParamV2(@RequestParam("username") String memberName, @RequestParam("age") int memberAge) {
log.info("username = {}, age = {}", memberName, memberAge);
return "ok";
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v3")
public String requestParamV3(@RequestParam String username, @RequestParam int age) {
// HTTP 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같으면 파라미터명 생략 가능
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v4")
public String requestParamV4(String username, int age) {
// String, int 등의 단순 타입이면 @RequestParam 도 생략 가능
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-required")
public String requestParamRequired(
@RequestParam(required = true) String username,
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
/**
* @RequestParam(required = false) int age
* 기본형 타입은 메모리의 할당된 공간에 직접 값을 저장하기 때문에, null 이 들어갈 수 없다. (500 예외 발생)
*
* 해결 방안
* 1. 래퍼클래스인 Integer
* 2. defaultValue 속성 추가
*/
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-default")
public String requestParamDefault(
@RequestParam(required = true, defaultValue = "guest") String username,
@RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "-1") int age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
/**
* 빈 문자의 경우에도 설정한 기본 값이 적용된다.
*/
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-map")
public String requestParamMap(@RequestParam MultiValueMap<String, String> multiValueMap){
// http://localhost:8080/request-param-map?username=ojg&age=32&age=31
log.info("username={}, age={}", multiValueMap.get("username"), multiValueMap.get("age")); // username=[ojg], age=[32, 31]
return "ok";
}
/**
* MultiValueMap
* @RequestParam 내 속성 required, defaultValue 속성을 신경 쓸 필요없다.
* 하지만 어떤 파라미터가 넘어오는지 명확하지 않아 불편하다.
*/
}
@ModelAttribute
1
2
3
4
5
6
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/model-attribute-v1")
public String modelAttributeV1(@ModelAttribute HelloData helloData) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", helloData.getUsername(), helloData.getAge());
return "ok";
}
HelloData 인스턴스 생성 후, 넘어온 파라미터 값을 해당 인스턴스에 set 해준다.
HTTP 요청 메시지
메시지 바디에 데이터를 직접 담아 값을 넘길 경우 @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute를 사용할 수 없다.
메시지바디의 데이터: TEXT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestBodyStringController {
@PostMapping("/request-body-string-v1")
public void requestBodyString(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("messageBody = {}", messageBody);
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
@PostMapping("/request-body-string-v2")
public void requestBodyStringV2(InputStream inputStream, Writer responseWriter)
throws IOException {
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody);
responseWriter.write("ok");
/**
* InputStream(Reader): HTTP 요청 메시지 바디의 내용을 직접 조회
* OutputStream(Writer): HTTP 응답 메시지의 바디에 직접 결과 출력
*/
}
@PostMapping("/request-body-string-v3")
public HttpEntity<String> requestBodyStringV3(HttpEntity<String> httpEntity) {
String messageBody = httpEntity.getBody();
log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody);
return new HttpEntity<>("ok");
/**
* 매개변수 HttpEntity 를 사용하여 HTTP header, body 정보를 편리하게 조회가능하다.
* return new HttpEntity<>("ok");: 응답에도 HttpEntity 사용 가능하다.
*
* HttpEntity
* 요청 HTTP header, message body 정보 조회
* 응답 또한 가능
*
* RequestEntity, ResponseEntity 둘 다 HttpEntity 상속 받음
*
* RequestEntity
* HttpMethod, url 정보가 추가, 요청에서 사용
* ResponseEntity
* HTTP 상태 코드 설정 가능, 응답에서 사용
* return new ResponseEntity<String>("Hello World", responseHeaders, HttpStatus.CREATED)
*/
}
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-string-v4")
public String requestBodyStringV4(@RequestBody String messageBody) {
log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody);
return "ok";
}
}
메시지바디의 데이터: JSON
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestBodyJsonController {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@PostMapping("/request-body-json-v1")
public void requestBodyJsonV1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody);
HelloData data = objectMapper.readValue(messageBody, HelloData.class);
log.info("username={}, age={}", data.getUsername(), data.getAge());
response.getWriter().write("ok");
/**
* 메소드의 리턴타입이 없을 경우 뷰 리졸버가 매핑된 url 명의 뷰를 찾아 반환한다.
*/
}
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-json-v2")
public String requestBodyJsonV2(@RequestBody String messageBody) throws
IOException {
HelloData data = objectMapper.readValue(messageBody, HelloData.class);
log.info("username={}, age={}", data.getUsername(), data.getAge());
return "ok";
}
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-json-v3")
public String requestBodyJsonV3(@RequestBody HelloData data) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", data.getUsername(), data.getAge());
return "ok";
/**
* HttpEntity, @RequestBody 를 사용하면 HTTP 메시지 컨버터가 HTTP 메시지 바디의 내용을 우리가 원하는 문자나 객체로 변환해준다.
*/
}
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-json-v4")
public String requestBodyJsonV4(HttpEntity<HelloData> httpEntity) {
HelloData data = httpEntity.getBody();
log.info("username={}, age={}", data.getUsername(), data.getAge());
return "ok";
}
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-json-v5")
public HelloData requestBodyJsonV5(@RequestBody HelloData data) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", data.getUsername(), data.getAge());
return data;
/**
* @RequestBody 요청: JSON 요청 -> HTTP MessageConvertor -> 객체
* @ResponseBody 응답: 객체 -> HTTP MessageConvertor -> JSON 응답
*/
}
}
리턴타입이 없고 @ResponseBody를 사용하지도 않았는데 뷰 리졸버가 실행되지 않고 메시지바디로 응답하는 이유는 뭘까?
HttpServletResponse, OutputStream(Writer) 를 파라미터로 받고 있으면 메시지 바디로 응답한다.
HTTP 응답
스프링(서버)에서 응답 데이터를 만드는 방법 3가지
정적 리소스: 웹 브라우저에 정적인 HTML, CSS, JS 를 제공할 경우뷰 템플릿 사용: 웹브라우저에 동적인 HTML을 제공할 경우HTTP 메시지 사용: HTTP API를 제공하는 경우 HTML이 아니라 데이터를 전달해야 하므로, HTTP 메시지 바디에 JSON 같은 형식으로 데이터를 실어 보낸다.
정적리소스
스프링 부트의 정적 리소스 클래스패스
/static , /public , /resources , /META-INF/resources뷰 템플릿
뷰 템플릿을 거쳐 HTML이 생성되고 뷰가 응답을 만들어서 전달한다.
뷰 템플릿 경로: src/main/resources/templates
뷰 템플릿 호출
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@Controller
public class ResponseViewController {
@GetMapping("/response-view-v1")
public ModelAndView responseViewV1() {
return new ModelAndView("response/hello").addObject("data", "hello!");
}
@RequestMapping("/response-view-v2")
public String responseViewV2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data", "hello!!");
return "response/hello";
}
@RequestMapping("/response/hello")
public void responseViewV3(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data", "hello!!");
}
}
HTTP API, 메시지 바디에 직접 입력
1
HTTP 응답 정리
- @ResponseBody가 없다면 뷰 리졸버가 실행되어 뷰를 찾고, 뷰가 응답을 만들어서 클라이언트에게 전달한다.
- @ResponseBody가 있다면 HttpMessageConverter가 사용되어 반환값을 적절한 형식(JSON, XML..)으로 변환 후 메시지 바디로 응답을 한다.
- 메시지 바디로 응답할 경우
- 메소드 단위에 @ResponseBody
- 클래스 단위에 @RestController
- 메소드 리턴타입으로 HttpEntity, ResponseEntity 반환
- 메소드 파라미터 값으로 HttpResponse, OutputStream(Writer)
HTTP Message Converter
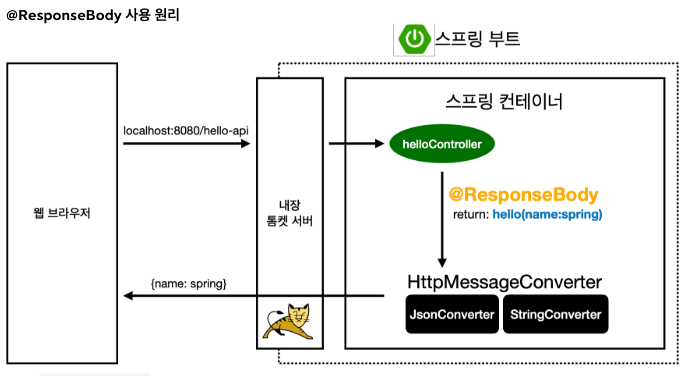
기본 문자처리: StringHttpMessageConverter
기본 객체처리: MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
응답의 경우 클라이언트의 HTTP Accept 헤더와 서버의 컨트롤러 반환 타입 정보 둘을 조합하여 HttpMessageConverter가 선택된다.
- HTTP 메시지 컨버터 적용
HTTP 요청: @RequestBody , HttpEntity(RequestEntity)
HTTP 응답: @ResponseBody , HttpEntity(ResponseEntity)
ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter
클래스 타입: byte[] , 미디어타입: /
요청 예) @RequestBody byte[] data
응답 예) @ResponseBody return byte[] 쓰기 미디어타입 application/octet-stream
StringHttpMessageConverter
클래스 타입: String , 미디어타입: /
요청 예) @RequestBody String data
응답 예) @ResponseBody return “ok” 쓰기 미디어타입 text/plain
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
클래스 타입: 객체 또는 HashMap , 미디어타입 application/json 관련
요청 예) @RequestBody HelloData data
응답 예) @ResponseBody return helloData 쓰기 미디어타입 application/json 관련
HTTP 요청 데이터 읽기
- HTTP 요청이 오고, 컨트롤러에서 @RequestBody , HttpEntity 파라미터를 사용한다.
- 메시지 컨버터가 메시지를 읽을 수 있는지 확인하기 위해 canRead() 를 호출한다.
대상 클래스 타입을 지원하는지, HTTP 요청의 Content-Type 미디어 타입을 지원하는지 확인한다.
예: @RequestBody 의 대상 클래스 ( byte[] , String , HelloData )
예: text/plain , application/json , / - canRead() 조건을 만족하면 read() 를 호출해서 객체 생성하고, 반환한다.
HTTP 응답 데이터 생성
- 컨트롤러에서 @ResponseBody , HttpEntity 로 값이 반환된다.
- 메시지 컨버터가 메시지를 쓸 수 있는지 확인하기 위해 canWrite() 를 호출한다.
대상 클래스 타입을 지원하는지, HTTP 요청의 Accept 미디어 타입을 지원하는지 확인한다.
예: return의 대상 클래스 ( byte[] , String , HelloData )
예: text/plain , application/json , / - canWrite() 조건을 만족하면 write() 를 호출해서 HTTP 응답 메시지 바디에 데이터를 생성한다.

참고
HTTP FORM 요청은 POST, GET만 사용할 수 있다.
PUT, PATCH는 HTTP API 전송시에 사용한다.
PRG(Post / Redirect / Get)를 해야하는 이유
POST 요청 후 저장프로세스를 실행 후 다른 페이지로 이동하였다 하더라도 URL은 그대로이다.
이 상태에서 계속 새로고침을 하게 되면 다중 저장이 발생하는 문제를 겪게 된다.
PRG
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV5(Item item) {
itemRepository.save(item);
return "redirect:/basic/items/" + item.getId();
}
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV6(Item item, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
Item savedItem = itemRepository.save(item);
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("itemId", savedItem.getId());
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("status", true);
return "redirect:/basic/items/{itemId}";
/**
* RedirectAttributes
* URL 인코딩, PathVariable, 쿼리 파라미터까지 처리해준다.
*
* http://localhost:8080/basic/items/3?status=true
*/
}
URL에 변수를 더해서 사용하는 것은 URL 인코딩이 안되기 때문에 위험하기에
RedirectAttributes를 사용하자.
1
<h2 th:if="${param.status}" th:text="'저장 완료!'"></h2>
